
-
ENERGY STORAGE
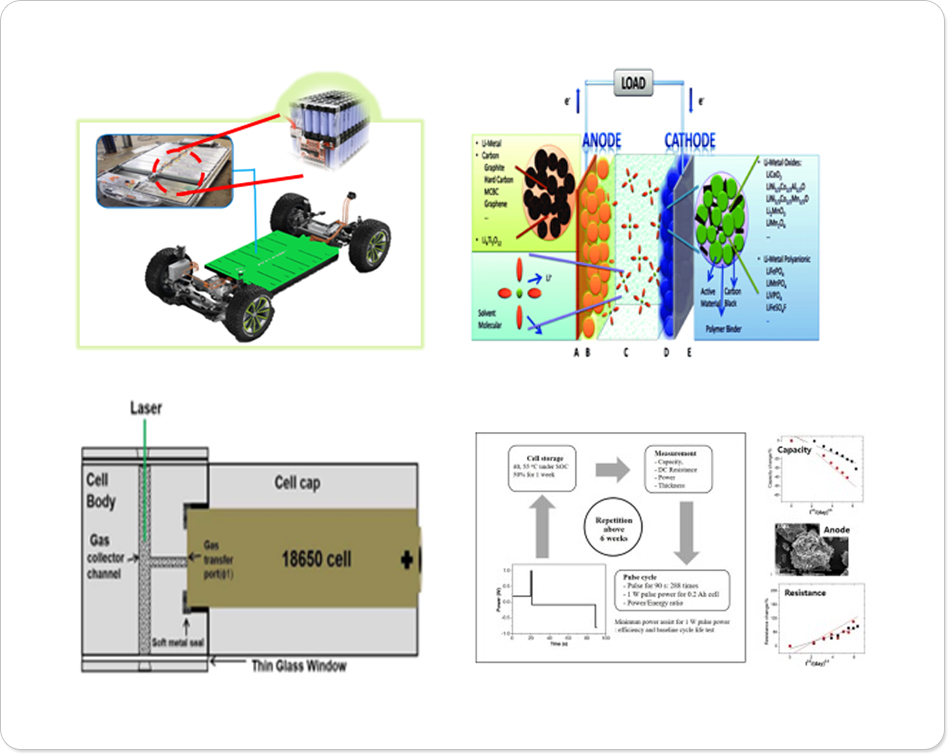
His appliance is loved by many users as they are light in weight for even a child to steer, but yet boast strong suction power.The birth of cordless vacuums was possible in large part due to Li-ion batteries. Lightweight, high energy density Li-ion batteries with high capacity and efficiency than other batteries are widely applied in diverse are as ranging from small appliances and IT devices to power tools, energy storage systems and electric vehicles.

- A Lithium-ion battery generates electricity through chemical reactions of lithium. This is why, of course, lithium is inserted into the battery and that space for lithium is called “cathode”. However, since lithium is unstable in the element form, the combination of lithium and oxygen, lithium oxide is used for cathode. The material that intervenes the electrode reaction of the actual battery just like lithium oxide is called ”active material”. In other words, in the cathode of a Li-ion battery, lithium oxide is used as an active material.

- When the battery is being charged, lithium ions are stored in the anode and not the cathode. At this point, when the conducting wire connects the cathode to the anode (discharge state), lithium ions naturally flow back to the cathode through the electrolyte, and the electrons (e-) separated from lithium ions move along the wire generating electricity. For anode graphite which has a stable structure is used, and the anode substrate is coated with active material, conductive additive and a binder. Thanks to graphite’s optimal qualities such as structural stability, low electrochemical reactivity, conditions for storing much lithium ions and price, the material is considered suitable to be used for anode.

- While the cathode and anode determine the basic performance of a battery, electrolyte and separator determine the safety of a battery. The separator functions as a physical barrier keeping cathode and anode apart. It prevents the direct flow of electrons and carefully lets only the ions pass through the internal microscopic hole. Therefore, it must satisfy all the physical and electrochemical conditions. Commercialized separators we have today are synthetic resin such as polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP).


